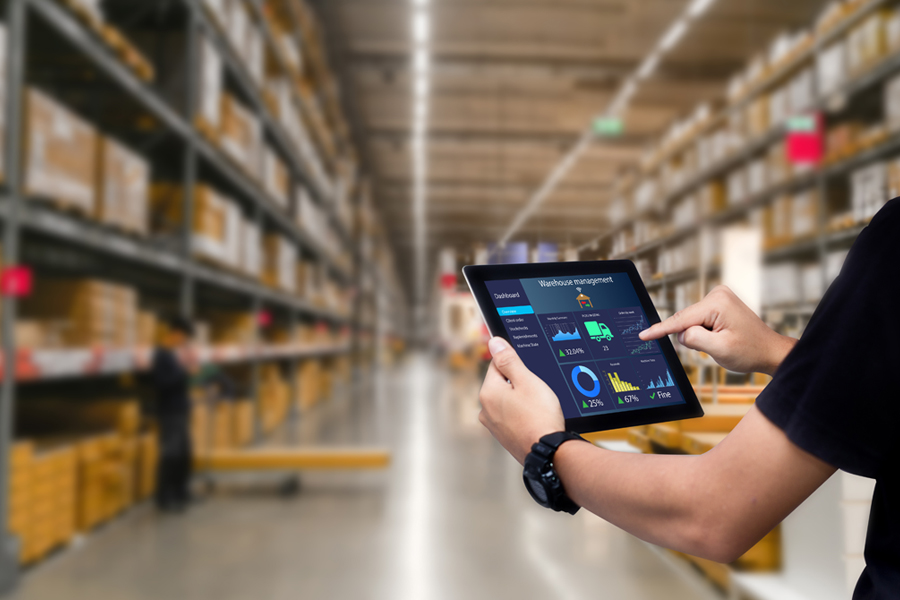
Create an effective Inventory Management system/Supply chain process
An effective inventory management system and supply chain process are crucial for optimizing operations, reducing costs, and meeting customer demands. Here’s a concise guide to creating such a system:
- Demand Forecasting: Utilize historical data, market trends, and customer insights to forecast demand accurately. Implement forecasting models and software to predict demand variability and seasonality.
- Inventory Classification: Classify inventory items based on demand variability, value, and criticality using techniques like ABC analysis. Allocate resources and focus inventory management efforts based on the classification.
- Safety Stock Management: Maintain safety stock levels to buffer against demand variability, lead time uncertainty, and supply chain disruptions. Set safety stock levels based on service level targets and demand forecast accuracy.
- Supplier Relationship Management: Cultivate strong relationships with suppliers to ensure timely deliveries, quality consistency, and cost-effectiveness. Collaborate closely with key suppliers to align production schedules and inventory levels.
- Inventory Optimization: Implement inventory optimization techniques such as Economic Order Quantity (EOQ), Just-In-Time (JIT), and Vendor-Managed Inventory (VMI) to minimize holding costs while meeting service level objectives.
- Inventory Tracking and Visibility: Utilize barcode scanning, RFID technology, and inventory management software to track inventory movements accurately. Ensure real-time visibility into inventory levels across multiple locations and channels.
- Warehouse Management: Optimize warehouse layout and operations to minimize picking, packing, and shipping times. Implement warehouse management systems (WMS) to automate inventory tracking, storage allocation, and order fulfillment processes.
- Transportation Management: Streamline transportation processes to minimize transit times, reduce costs, and improve reliability. Utilize transportation management systems (TMS) to optimize route planning, load consolidation, and carrier selection.
- Reverse Logistics: Develop efficient processes for managing returns, exchanges, and product recalls. Implement reverse logistics systems to streamline product disposition, refurbishment, or disposal while minimizing costs and environmental impact.
- Continuous Improvement: Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) such as inventory turnover, fill rate, and order cycle time to identify areas for improvement. Implement lean principles and Kaizen methodologies to continuously optimize inventory management processes.
- Risk Management: Identify and mitigate supply chain risks such as supplier disruptions, geopolitical issues, and natural disasters. Develop contingency plans and alternative sourcing strategies to maintain business continuity.
- Collaboration and Integration: Foster collaboration and information sharing across internal departments and external partners to align inventory management efforts with broader business goals and supply chain objectives.